Dietary changes may treat pulmonary hypertension
Science Daily - Heart Disease
MAY 2, 2024
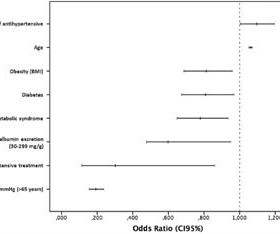
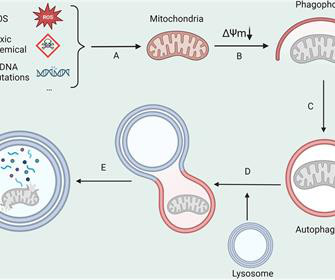
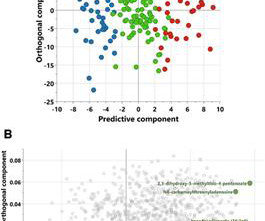
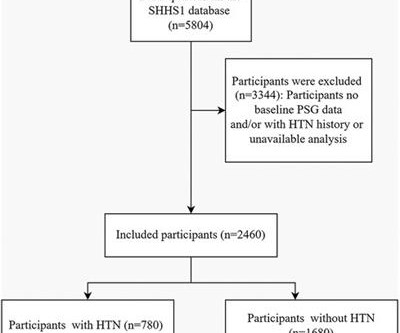
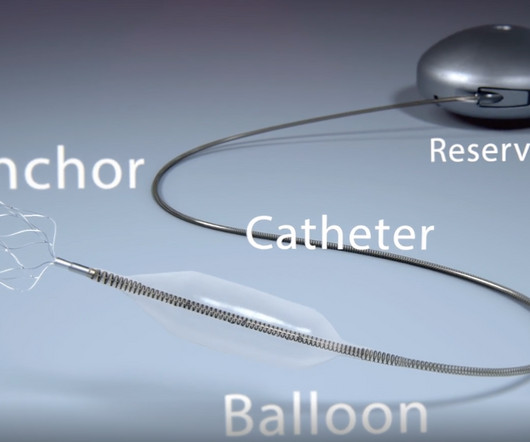
This difference becomes clear in pulmonary hypertension, in which only the lungs' blood vessels stiffen progressively, leading to chronic lung disease, heart failure and death.


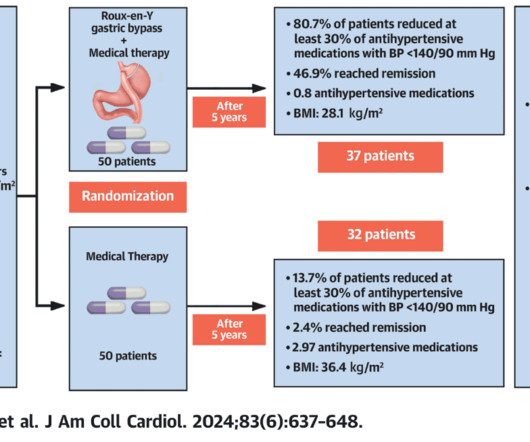

















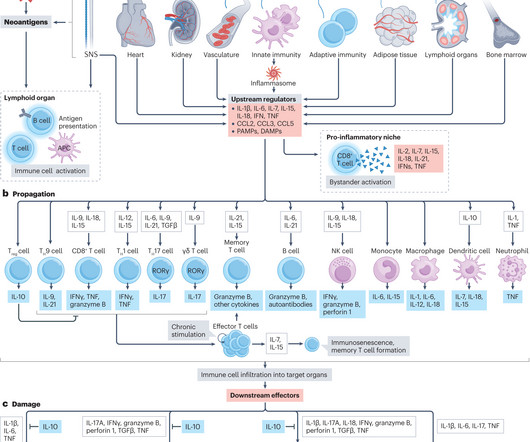
















Let's personalize your content