ECG Blog #415 — The Cath showed NO Occlusion!
Ken Grauer, MD
FEBRUARY 3, 2024
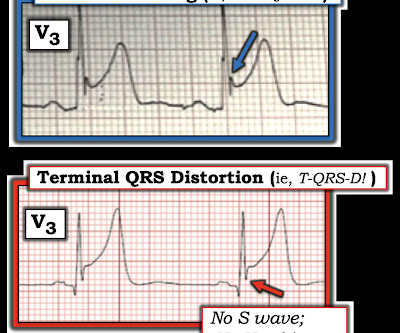
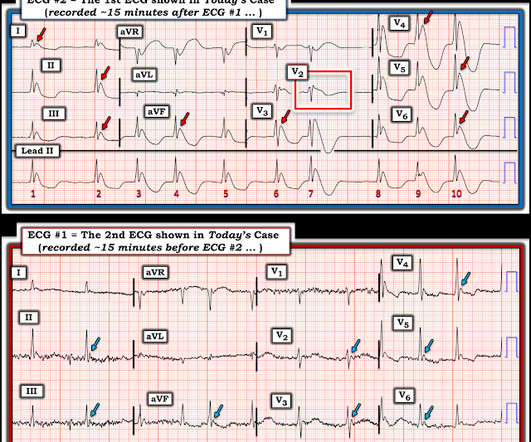
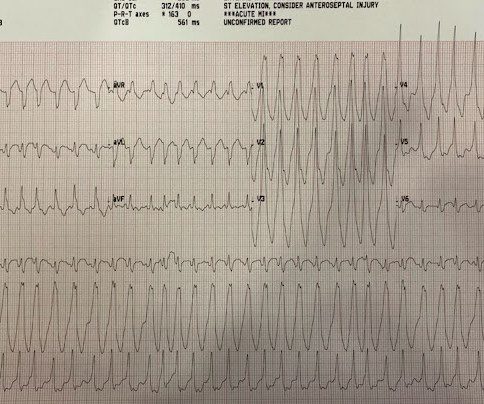
Today’s patient is an older woman who experienced a number of fainting epiodes over the previous week. No CP ( C hest P ain ). Shortly after arrival in the ED ( E mergency D epartment ) — she suffered a cardiac arrest. The ECG in Figure-1 was obtained following successful resuscitation. Stat Echo — obtained shortly after successful resuscitation revealed anterior wall akinesis.




















Let's personalize your content