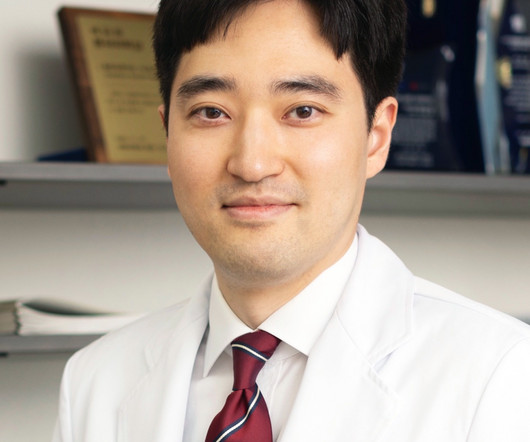
ASN Releases New Guidance on Obesity Management in Kidney Disease
HCPLive
SEPTEMBER 18, 2024
The new guidance reviews existing tools for weight management and provides recommendations for their use in clinical practice in patients with obesity and kidney disease.










































Let's personalize your content