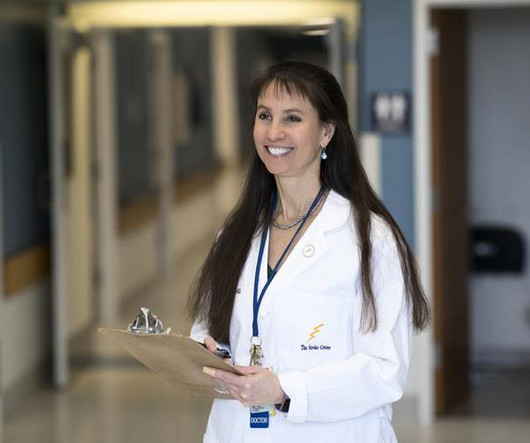
Stroke recovery: It's in the genes
Science Daily - Stroke
JULY 24, 2024
New research has found that specific genes may be related to the trajectory of recovery for stroke survivors, providing doctors insights useful for developing targeted therapies.






































Let's personalize your content