Protein discovery could help prevent cancer treatment-related heart damage
Science Daily - Heart Disease
JUNE 3, 2024
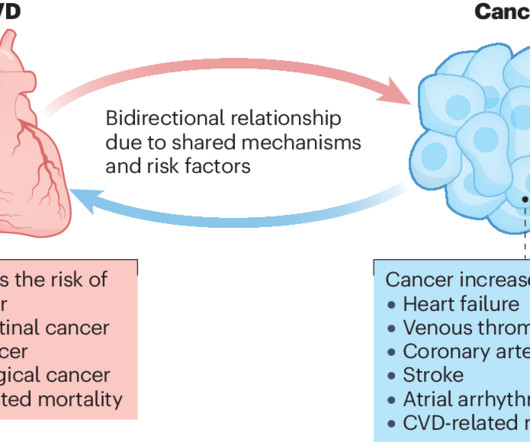
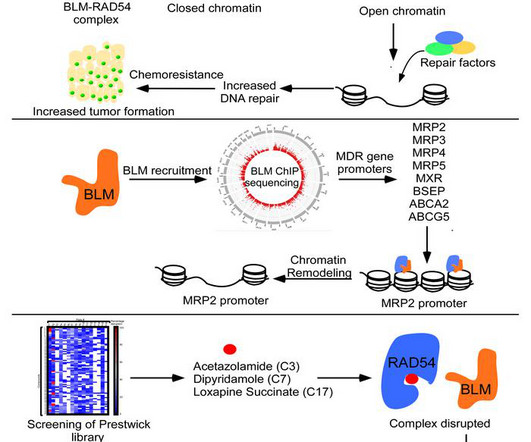
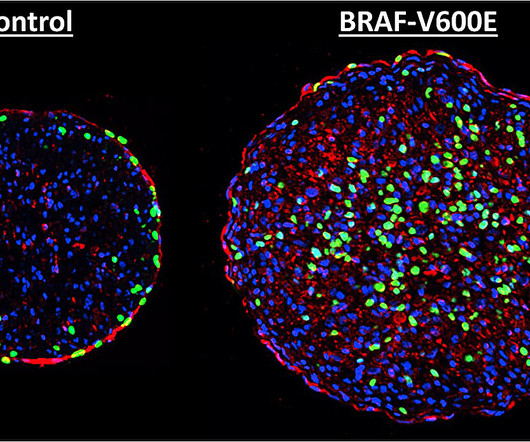
Blocking a protein known as CDK7 could prevent heart damage associated with a commonly used cancer chemotherapy medication, according to a new study. Importantly, the researchers also found that inhibiting CDK7 could help enhance the medication's cancer-killing capability.







































Let's personalize your content